Lupus Nephritis
Uncover what other tests can’t see with AVISE® SLE Monitor, the most advanced autoimmune testing available.
Know more with
AVISE® SLE Monitor
The most advanced assessment available
With a powerful combination of biomarkers that go beyond standard SLE tests, AVISE® SLE Monitor empowers you with the full intel to stay a step ahead of flare ups, regularly monitor disease progression, assess treatment efficacy, and help prevent premature disease advancement and long-term damage.

A more advanced assessment requires a more comprehensive biomarker suite

ES4d is informative even when C3/C4 is unchanged
In a cohort of 124 SLE patients that were followed longitudinally, levels of EC4d fluctuated with disease activity and provided additional information regardless of changes in C3/C4 levels.
Fluctuating C3/C4 Levels
Chronic Low or Normal C3/C4 Levels
Marginal R2 =7.9% (p <0.001)

Superior detection of organ involvement
Anti-C1q: Identify the risk of Lupus Nephritis
Anti-C1q is superior to other biomarkers in association with SELENA-SLEDAI values and lupus nephritis. SLE patients with positive levels are 2X more likely to have renal involvement.3
Superior detection of changes in disease activity
EC4d: More accurate monitoring
Our proprietary CB-CAPs EC4d test has strong correlation with disease activity and levels decline rapidly with clinical improvement.4
Anti-dsDNA by CIA: Superior accuracy
Chemiluminescence immunoassay (CIA) has expanded dynamic range and demonstrated superior agreement with the Farr assay.1

Superior detection of Lupus Nephritis
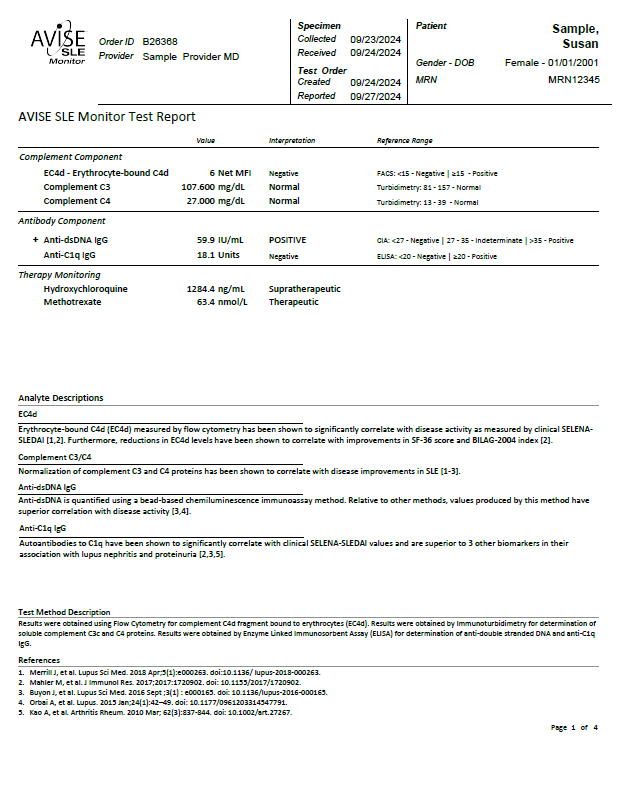
Clinical Utility: AVISE SLE Monitor Test Report
The AVISE SLE Monitor test should be considered any time the condition of a SLE patient is being assessed.
If the patient is also being monitored with AVISE® HCQ, the AVISE SLE Monitor test report will also include an AVISE HCQ test result page.
References:
- Merrill J, et al. Erythrocyte-bound C4d in combination with complement and autoantibody status for the monitoring of SLE. Lupus Science and Medicine. 2018.
- Orbai, A.-M., Truedsson, L., Sturfelt, G. et al. (2015). Anti-C1q antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus, 24(1): 42–49.
- Akhter E, Burlingame R, Seaman A, et al. Anti-C1Q antibodies have a higher correlation with flares of lupus nephritis than other serum markers. Lupus. 2012.
- Buyon J, et al. Reduction in erythrocyte-bound complement activation products and titres of anti-C1q antibodies associate with clinical improvement in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus Science and Medicine. 2016.